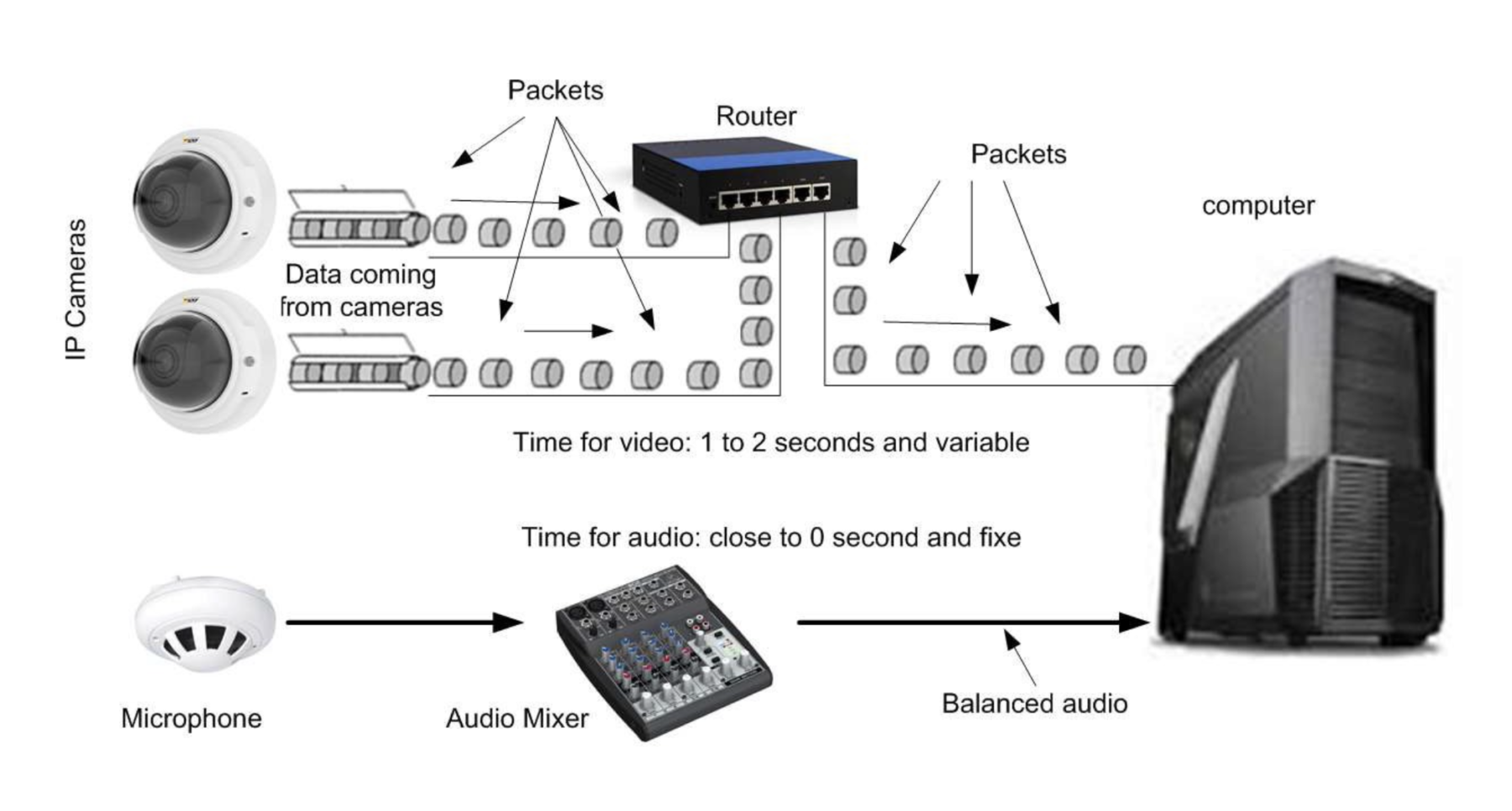
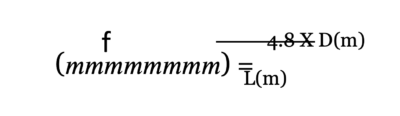Presenting Tech Tip Tuesdays! Where broadcast experts answer your commonly asked A/V questions!
Do you have an A/V question you’d like us to answer? Send it to info@maestrovision.com and it just might be featured in a future video!
Question
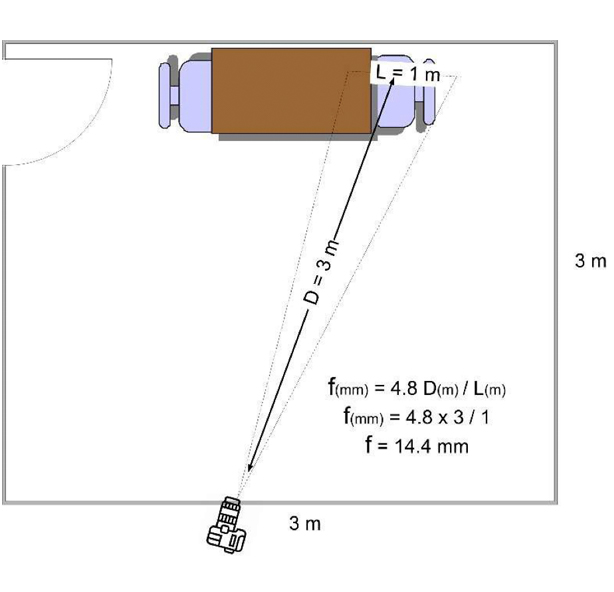
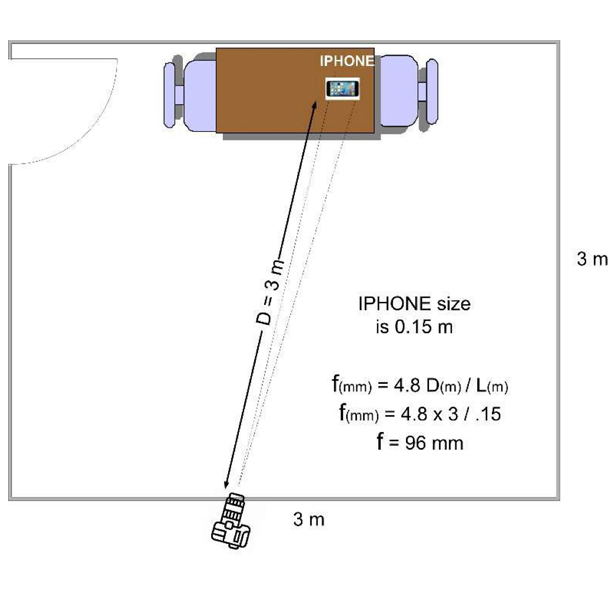
How Many Cameras do you Recommend for an Interview Room?
Answer
We recommend strategically placing two cameras in an interview room.
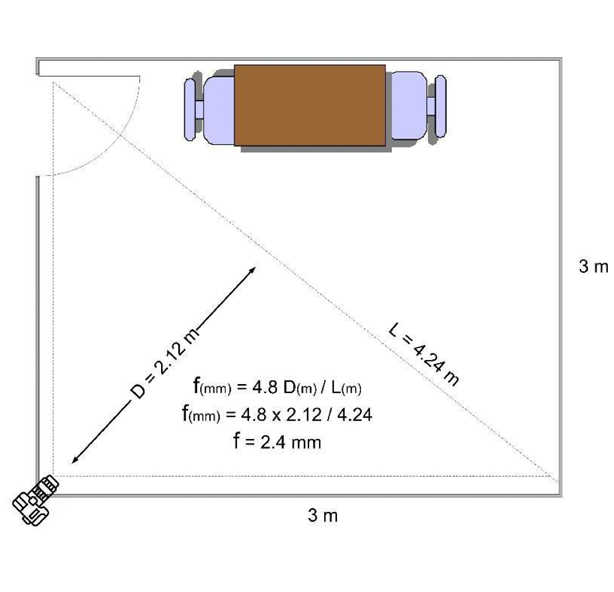
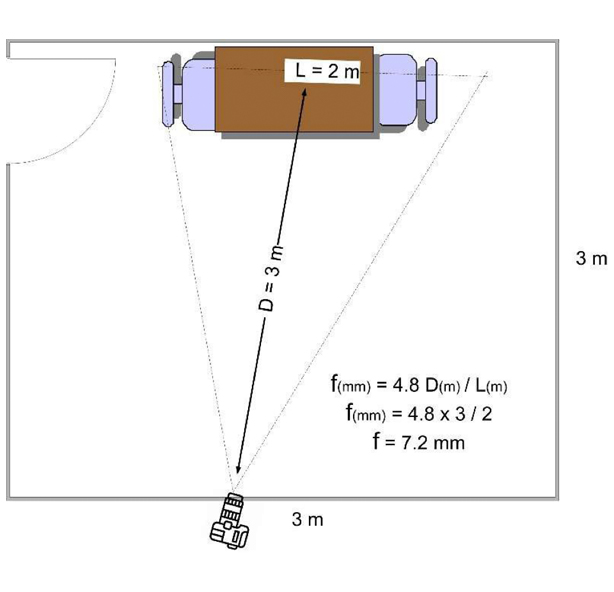
The first should be a wide-angle camera positioned in a corner where it can capture the entire room.
For the second camera, position a varifocal one to capture both the interviewee’s full body and the corner where the first camera is placed.
If there’s a whiteboard or any other object in the room you want to be recorded, make sure to position a third camera if not already captured.
Interview recording requirements vary for each organization, therefore the number and placement of cameras depend on your specific needs.
Read More